HSRP - Deployment in Distribution Layer
Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) is a First Hop Redundancy Protocol (FHRP) designed to provide redundant gateways for end-user devices. When deploying HSRP at the Distribution Layer, ensure that connections to Access switches are via Layer 2. The SVIs (Switched Virtual Interfaces) configured with HSRP must be on the same broadcast domain to communicate effectively.
Assuming the use of a Layer 3 switch, there are two choices for the communication between the redundant gateways:
Layer 2 Link Between Distribution Switches
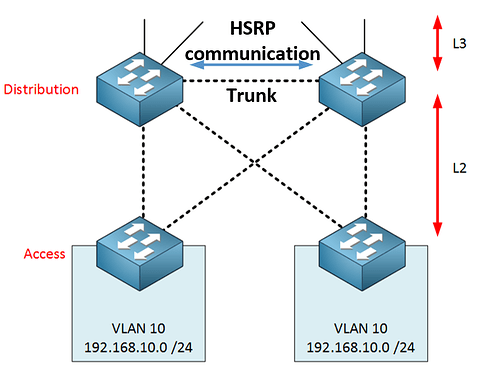
- Use a trunk link that includes the VLANs for the SVIs using HSRP.
- HSRP messages are sent directly over the Layer 2 link.
- Creates a Layer 2 loop, requiring Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to block one port to prevent the loop.
- Set STP priorities so the active HSRP switch is the STP root bridge and the standby is the secondary root bridge.
Layer 3 Link Between Distribution Switches
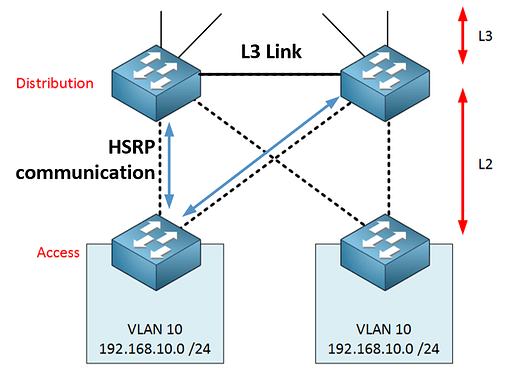
- The Layer 3 link cannot be used to exchange HSRP messages.
- SVIs communicate over Layer 2 links with Access switches.
- Avoids Layer 2 loops, eliminating STP issues.
- Results in fewer redundant links.
Choosing between the two cases depends on the specific network requirements and trade-offs between redundancy and potential STP issues. Adjust STP root bridge priorities accordingly to optimize network performance.
Links
https://networklessons.com/cisco/ccie-enterprise-infrastructure/hsrp-hot-standby-routing-protocol/